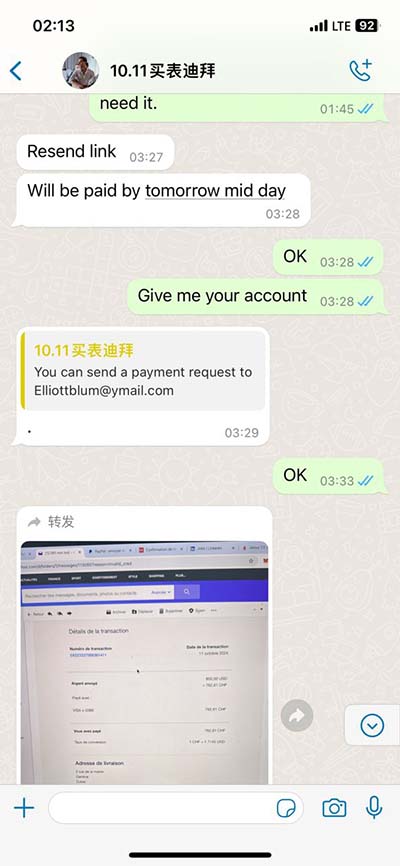
lv candi cm2 | Left Ventricular Dimensions lv candi cm2 The LV dimensions must be measured when the end-diastolic and end-systolic valves (MV and AoV) are closed in the parasternal long axis (PLAX) view. The measurement . Amazon.com: E LV Galaxy S7 Edge Case - Hybrid Armor Defender Slim Shock Absorption Bumper Case for Samsung Galaxy S7 Edge - (Grey/Mint) : Cell Phones & Accessories
0 · Recommendations for Cardiac Chamber Quantification by
1 · Left Ventricular Dimensions
Abonē mail+. Bez reklāmas un ierobežojumiem. Stabils un drošs 20 GB bezmaksas e-pasts, foto, spēles, faili, iepazīšanās un citas Inbox.lv sadaļas ar vairāk nekā 15 gadu pieredzi un miljonu reģistrēto lietotāju uzticamību!
The LV dimensions must be measured when the end-diastolic and end-systolic valves (MV and AoV) are closed in the parasternal long axis (PLAX) view. The measurement .tricular [LV] size and ejection fraction [EF], left atrial [LA] volume), outcomes data are lacking for many other parameters. Unfortunately, this approach also has limitations. The LV dimensions must be measured when the end-diastolic and end-systolic valves (MV and AoV) are closed in the parasternal long axis (PLAX) view. The measurement is performed in the basal portion of the LV by the chordae.tricular [LV] size and ejection fraction [EF], left atrial [LA] volume), outcomes data are lacking for many other parameters. Unfortunately, this approach also has limitations.
Recommendations for Cardiac Chamber Quantification by
Left Ventricular Dimensions
Assessment of LV function remains the most common reason for cardiac imaging because of its powerful ability to predict morbidity and mortality. Current routine methods of quantifying LV function (with LVEF) is not without limitations.LV volumes are calculated from a “full volume” data set (raw data). Perform on an LV focused volume (atria are not imp ortant). o Focus on including the entire LV in the pyramidal dataset and obtaining good endocardial border definition. On most .
Left ventricular mass (LVM) is a well-established measure that can independently predict adverse cardiovascular events and premature death. 1-3 Population-based studies have revealed that increased LVM and left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) as assessed by two-dimensional (2D) M-mode echocardiography measurements provide prognostic information be.
Objectives: To assess the sex-differences in the progression, LV remodelling and long-term outcome of native AS. Methods: Baseline and follow-up echocardiographic data of patients with at least mild-to-moderate AS [aortic valve area (AVA)≤1.5 cm2, maximum aortic velocity (Vmax) ≥2.5 m/s or mean gradient (MG)≥25 mmHg] were prospectively .
Stage D is defined as symptomatic severe AS, which can be further categorized as high-gradient severe AS with normal ventricular function (stage D1), low-gradient severe AS with a velocity less than 4 m/s but valve area less than or equal to 1.0 cm 2 due to LV systolic dysfunction (stage D2), and low-gradient severe AS with a small LV chamber .New reference intervals for linear LV dimensions and LV mass are presented in Table 2. LV dimensions should be obtained from the parasternal long-axis (PLAX) window preferentially using 2D imaging. Results. The study population was predominantly male (61%) with a median age of 62 (53–72) years (table 1). Male patients tended to be older (64 vs 59 years) with a larger LV diameter (5.4 vs 4.6 cm) and LV indexed volume (72 vs .
They evaluated the reproducibility of LV dimension, area, volumes, and indices of systolic function by 2D echocardiography in a cohort of 169 children (mean age, 9.5 years; range, 0.2–20.6 years) with dilated cardiomyopathy.
The LV dimensions must be measured when the end-diastolic and end-systolic valves (MV and AoV) are closed in the parasternal long axis (PLAX) view. The measurement is performed in the basal portion of the LV by the chordae.tricular [LV] size and ejection fraction [EF], left atrial [LA] volume), outcomes data are lacking for many other parameters. Unfortunately, this approach also has limitations.Assessment of LV function remains the most common reason for cardiac imaging because of its powerful ability to predict morbidity and mortality. Current routine methods of quantifying LV function (with LVEF) is not without limitations.LV volumes are calculated from a “full volume” data set (raw data). Perform on an LV focused volume (atria are not imp ortant). o Focus on including the entire LV in the pyramidal dataset and obtaining good endocardial border definition. On most .
Left ventricular mass (LVM) is a well-established measure that can independently predict adverse cardiovascular events and premature death. 1-3 Population-based studies have revealed that increased LVM and left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) as assessed by two-dimensional (2D) M-mode echocardiography measurements provide prognostic information be. Objectives: To assess the sex-differences in the progression, LV remodelling and long-term outcome of native AS. Methods: Baseline and follow-up echocardiographic data of patients with at least mild-to-moderate AS [aortic valve area (AVA)≤1.5 cm2, maximum aortic velocity (Vmax) ≥2.5 m/s or mean gradient (MG)≥25 mmHg] were prospectively . Stage D is defined as symptomatic severe AS, which can be further categorized as high-gradient severe AS with normal ventricular function (stage D1), low-gradient severe AS with a velocity less than 4 m/s but valve area less than or equal to 1.0 cm 2 due to LV systolic dysfunction (stage D2), and low-gradient severe AS with a small LV chamber .
New reference intervals for linear LV dimensions and LV mass are presented in Table 2. LV dimensions should be obtained from the parasternal long-axis (PLAX) window preferentially using 2D imaging.
Results. The study population was predominantly male (61%) with a median age of 62 (53–72) years (table 1). Male patients tended to be older (64 vs 59 years) with a larger LV diameter (5.4 vs 4.6 cm) and LV indexed volume (72 vs .

The Freedom arc-resistant MCC is tested and verified per IEEE guideline C37.20.7, CSA standard 22.2 No. 0.22-11 and IEC TR 61641; Type 2 accessibility rating ensures arc-resistance around entire perimeter of MCC; Engineered with reinforced steel, latches and hinges to provide containment of internal faults inside a space-effective package
lv candi cm2|Left Ventricular Dimensions